
Optimize depot-to-customer deliveries with capacity-aware vehicle routing

Timefold’s maintenance scheduling Planning AI automates and optimizes your technicians’ schedules to reduce overall downtime and achieve higher operational efficiency.

Introduction to
In a Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP), optimizing your vehicle routes to visit customer locations efficiently is crucial. By reducing overall driving time, you can achieve significant benefits such as a 25% reduction in time spent on the road, lower fuel consumption and increased employee productivity.
A Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) is a optimization problem for which each customer is visited exactly once by one of the vehicles. A solution decides for each vehicle which customers to visit and in which order, while minimizing the driving time and adhering to constraints.
Building effective Vehicle Routing management software is complex. There are various constraints to keep into account to ensure operational efficiency. For instance: vehicle capacity, driver skill, traffic, …At Timefold we support software builders with the right toolbox to tackle these hard mathematical problems. Our VRP model helps companies to manage their fleet of vehicles efficiently and reduces wasteful planning.
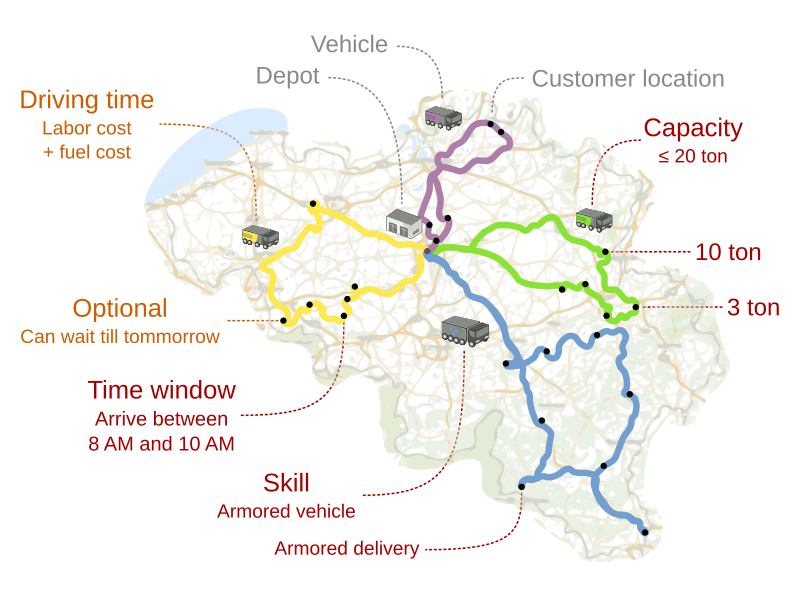
Like other Optimization problems, the Vehicle Routing Problem has Constraints. Constraints define the rules and objectives of the VRP solution. We distinguish between hard and soft constraints
Hard constraints represent limitations or requirements that cannot be violated.
They are often essential for ensuring the feasibility, practicality or following business rules and SLAs of the optimized solution. Failure to satisfy a hard constraint would render the solution infeasible, impractical, in contradiction to legislation for implementation.
Hard constraint examples in VRP:
Soft constraints represent a cost reduction, preferences, service quality, employee wishes, …Meeting them is desirable but not mandatory for a feasible planning solution.
Whilst optimizing a VRP, goals can be to minimize costs, driving time, or distance. It’s key to be able to differentiate and combine these or other business goals for the best outcome.
Driving time optimization, a vital VRP aspect, seeks to reduce the total time vehicles spend on the road considering traffic conditions, speed limits, and more.
Another crucial aspect is driving distance optimization. Shorter distances lead to less fuel usage and vehicle wear, reducing costs. Using elements like the shortest path, road conditions, and vehicle characteristics to determine optimal routes.
Total cost optimization in VRP extends to maintenance costs, driver wages, vehicle depreciation, and opportunity costs from inefficient routing.
To precalculate road costs Timefold can be integrated with other technologies. Typical solutions precalculate road costs include GraphHopper (embeddable, offline Java engine), Open MapQuest (web service) and Google Maps Client API (web service).
As the number of customers and vehicles increases, the possible combinations grow exponentially, making exhaustive search infeasible. Additionally, incorporating constraints like time windows and capacity limits further escalates the complexity.
In Computer Science, VRP is classified as an NP-Hard problem. That means it’s notoriously hard to scale out. A mathematical planning optimization solver like Timefold has a proven track record of dealing with this complex matter.
When handling day-to-day planning for vehicle routing you need your planning software to offer you:
Whilst there are various variations of the Vehicle Routing Problem they are mainly the basic Vehicle Routing Problem with specific constraints added to it.
A non-exhaustive list:

Optimize depot-to-customer deliveries with capacity-aware vehicle routing

Timefold’s maintenance scheduling Planning AI automates and optimizes your technicians’ schedules to reduce overall downtime and achieve higher operational efficiency.